
Woodkern/iStock Editorial via Getty Images
Investment Thesis
In the last decade, the automobile industry has been making a shift from internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles to battery electric vehicles (BEV). Rigorous research focusing on creating autonomous vehicles with intelligent systems and sleek designs has brought in new tech-savvy players in the industry. Global sales of electric cars have kept rising strongly in 2022, with 2 million sold in the first quarter, up 75% from the same period in 2021. Consequently, according to BCG Report, demand for lithium is expected to shoot up by a CAGR of more than 25% from now until 2030.
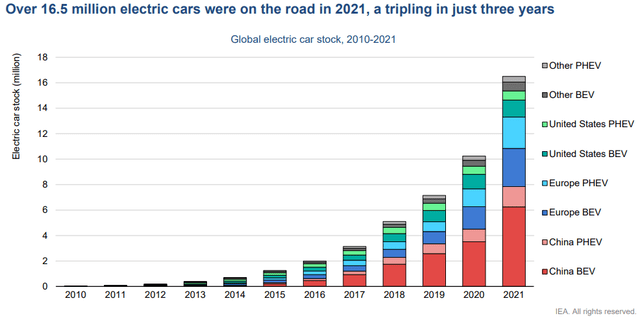
EIA
The Auto Manufacturing industry has faced many supply chain challenges with the shortage of semiconductors, high raw material prices, and demand and supply volatility caused by the pandemic. Interest in EVs and tax credits should help the industry grow further in the long run.
A little late to the party, but finally, Honda Motor Company (NYSE:HMC) has shown its interest in being fully electrified and partially autonomous by partnering up with Sony. The Japan-based company’s stock has also exhibited a downward trend in line with the stock market, losing about 14% YTD, compared to the S&P 500’s almost 20% loss.
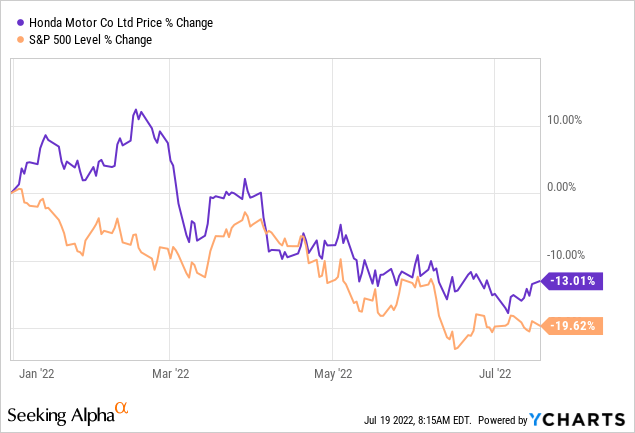
As the auto industry markets revive and production levels return to pre-Covid levels, I expect Honda Motor to show long-term bullish movement, especially with its aggressive move toward the EV market.
Company Overview
Tokyo-based Honda Motor Company is one of the leading car manufacturers in the world, which started as a bicycle engine manufacturer in the 1950s. It operates in over 150 markets worldwide, with more than 80 Japanese and 259 overseas subsidiaries.
The company manufactures and distributes motorcycles, automobiles, life creations, and financial services. Its core competence lies in manufacturing engines, and it is also developing its proprietary solid-state batteries.
Honda is the world’s top motorcycle manufacturer, with a strong position in Asia’s motorcycle markets. The segment contributed 15% of total sales revenue in 2022, with approximately 86% of total units sold in Asia.
The automobile segment generated 63% of the total sales revenue in 2022, with approximately 50% sold in Asia, followed by 31% in North America and 13% in Japan.
Approximately 44% of Honda’s power product units on a group basis were sold in North America, followed by 24% in Asia and 19% in Europe.
Aggressive Move Toward The EV Market
The global electric vehicle market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 18.2% and reach $823.75 billion by 2030. Honda aims to achieve carbon neutrality following the regulations and attributes of each sales region, including customer acceptance, the infrastructure environment, and the spread of renewable energy.
Accordingly, the company has aggressively partnered with companies concerning its expansion in the EV domain. It is progressing on its all-solid-state battery technology, which it sees as the core element of future EVs. The company aims to build a demonstration line to produce all-solid-state batteries with an investment of approximately 43 billion yen ($310 Million), accelerating the research to start demonstration production in Spring 2024.
The company’s 10-year trajectory includes an allocation of 5 trillion yen (over $36 billion) for electrification and software technologies, including R&D and separate investments. The company plans to launch 30 EV models globally by 2030, producing over 2 million units annually.
Partnerships and Joint Ventures
Recently, Sony and Honda announced a 10 billion yen ($74 million) joint ventu
re to create a new EV company known as Sony Honda Mobility Inc. The company will be established later this year, where Honda will be responsible for manufacturing and Sony will develop the mobility service platform. The company estimates deliveries to begin by 2025.
At the same time, Honda and General Motors (GM) have already enjoyed a close working relationship in the past. The two companies have previously worked on several projects, including the co-development of a next-generation fuel cell system and hydrogen storage technologies. In 2018 Honda and GM partnered to develop battery modules.
The two companies have announced a collaboration that aims to co-develop a series of affordable electric vehicles based on new global architecture using next-generation Ultium battery technology. According to the press release, this EV series is expected to go on sale in 2027, starting in North America.
In 2022, Honda has already announced the construction of two new EV plants with its partners, GAC Honda Automobile and Dongfeng Honda Automobile in China where an estimated 240,000 units are to be rolled out by the end of 2024.
Some sources also suggest that Honda also plans to enter into a joint venture with LG Energy Solutions, which already has a share of more than 30% in the global EV battery market. Both companies haven’t confirmed this speculation, But Honda’s intent is clearly to penetrate the phenomenally growing EV market.
This rapid growth can be attributed to rising fuel prices, as consumers tend to inject a one-time capital investment rather than paying high fuel costs. This has led to EVs having a much lower total ownership cost (TOC) than ICE vehicles.
Financial Brief
Honda’s liquidity of $30 Billion in the MRQ is strong enough to carry out its expansion plans into the EV market through various partnerships and joint ventures. The levered FCF of $7.49 billion is ample enough for Honda to continue its expansion and explore the EV domain, covering the company’s heavy R&D expenditure of $6.4 billion.
The possibility of various factors, such as recession-induced market contraction and financial and foreign exchange market volatility, may adversely affect liquidity since the company’s major markets are located in Asia. However, Honda’s financial services subsidiaries have committed equivalent to $9 billion in lines of credit that serve as alternative means of liquidity.
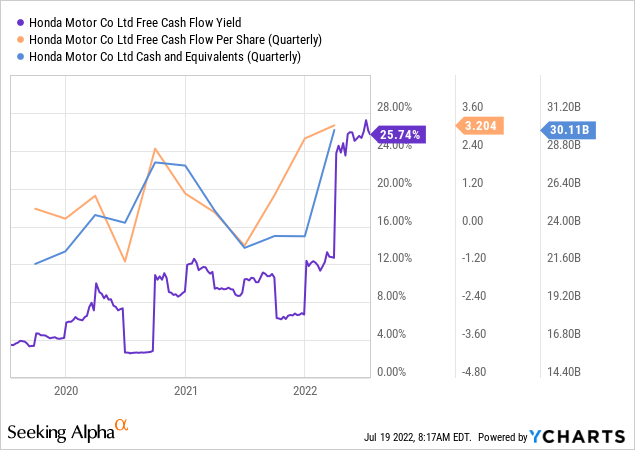
Honda has experienced a decrease in its automobile business by 7.4% from the previous fiscal year during 2022, mainly attributed to the sudden global shortages of semiconductor chips and the rise in raw material costs. In contrast, the Cash flow from operations was reported at $13.08 billion, an increment of 67% from its 5-years average, primarily due to higher operating assets. This exhibits that the company should be able to move back on its track as the macroeconomic negators subside.
Valuation
The company’s capital structure consists of $69.18 billion of debt with no short-term obligations, leading to a Total Debt to Equity ratio of 78.17%. This would generally be a cause for concern but is supposedly fine for a company like Honda, which is an experienced and mature player in the industry.
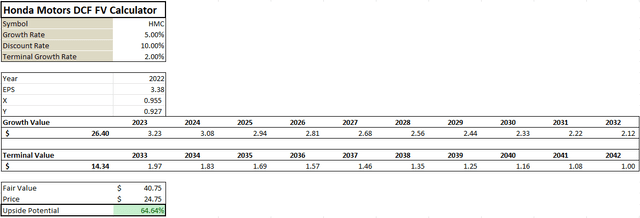
Currently, Honda is trading at a price level of $24.75 with a market cap of almost $42 Billion. Suppose we calculate the fair value using an EPS-based DCF model and plug-in conservative growth rate of 5%, comparatively higher cost of capital at 10% because of the high leverage, and a 2% terminal rate. In that case, Honda HMC’s fair value is estimated at $40.75, an upside of almost 65%. Comparatively, the analysts’ price target is $31.5.
Author
The last time the company traded at above $40 per share was in 2013 but given the aggressive growth in the EV market, the company is likely to hit the target price when it starts demonstrating prominent progress in its new endeavor by mid-2024.
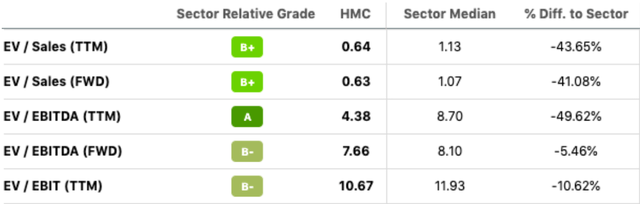
Either way, the stock price is undervalued, with almost all relative valuation multiples lower than its peers. The P/CF multiple is 3.14x against the sector median of 8.57x and the forward P/E multiple is 7.13x against the industry’s 12.22x. Wall Street analyst has also given a strong buy rating to Honda HMC.
Seeking Alpha
Conclusion
The automotive industry has witnessed several production challenges due to shortages in the semiconductor chip and high costs of raw materials. Similarly, high inflation and rising interest rates may also affect the growth in demand.
Even though the semiconductor shortage has hurt Honda sales, but the demand for the company’s products is still very strong. Moreover, the Japanese industry, in general, is heavily dependent on foreign suppliers for substantia
lly all its raw materials, and the consumer discretionary industry has largely been impacted by inflation and rising prices.
Macroeconomic factors have played a major role in consumer behavior towards spending. Despite the challenges, Honda’s strategy of collaborating with top-tier technology and automobile companies in transforming their automobile sector towards electrified vehicles can be a game-changer in coming years.
I rate the stock as a long-term buy and hold, as the company has the potential to generate substantial price returns as it executes its EV initiatives.
